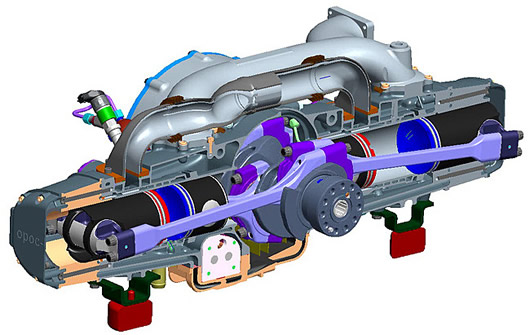
Six-stroke Engine
The six-stroke engine as we categorize today is classified as another type of an internal combustions engine apart from the two-stroke and the four- stroke engine types. Basically the construction of the six-stroke engine was initially meant to enhance the efficiency as well as to reduce exhaust emissions of engines based on the four-stroke engine. Over the years, engineers have managed to develop two types of six-stroke engines but with a twist in their concepts since the 90s.
First Concept:
As we know stroke in this sense means cycle therefore the six-stroke engine gains its name due to its six cycle process. At the beginning of the approach, the heat lost from the normal four-stroke Otto-cycle engine is captured and used to power and extra power and exhaust stroke meaning that the amount of heat lost by the normal four-stroke engine is used to add in an extra two cycles to the six-stroke engine. This doesn’t mean that the six-stroke engine is made of two engines; in fact it’s actually just a slight modification to the four-stroke engine by adding two extra strokes or in simpler understanding ‘cycles’ of the piston in the same combustion chamber or cylinder.
So what are the two extra strokes included?
As we know, the four-stroke engine has four cycles, two cycles each for the intake and the exhaust. Well the six-stroke however has three (3) cycles each which means the piston in this engine type moves up and down three (3) times for each fuel intake. So in addition to the four-stroke engine which has only one power stroke which is the fuel intake, the six-stroke has two power intakes before combustion which is first the fuel intake and the second consisting of either air or steam. This concept of the six-stroke engine also has three (3) separate designs:
- The Crower Six-stroke Engine (invented in the U.S by Bruce Crower)
- The Bajulaz Engine (developed by a Switzerland company, Bajulas S.A)
- The Velozeta Six-stroke Engine (developed by The College Of Engineering at Trivandrum, India)
Second Concept:
The other concept of the six-stroke engine type uses not one but two pistons opposing each other in a single combustion chamber or cylinder. In this concept however, the opposing pistons moves only half the cycle rate of the main piston therefore adding up to a total of six piston movement per cycle. The second piston or the opposing piston in this case replaces the functions of the valve of a normal four-stroke engine where the result produces an increase in the compression ratio of the system. This concept also has two divided designs both independently developed:
- The Beare Head Engine (invented by an Australian named Malcolm Beare)
- The German Charge Pump (invented by Helmut Kottmann)
شش زمانه موتور
این موتور شش زمانه ما امروز طبقه بندی به عنوان یکی دیگر از نوع یک موتور داخلی combustions به غیر از دو زمانه و چهار زمانه انواع موتور طبقه بندی شده است. در واقع ساخت و ساز موتور های شش زمانه قرار بود به منظور افزایش بهره وری و همچنین به منظور کاهش انتشار گازهای خروجی از موتورهای بر اساس موتور چهار زمانه. در طول این سالها، مهندسان موفق شده اند به دو نوع از موتورهای شش زمانه، اما با پیچ و تاب و در مفاهیم خود را از آنجا 90s.
مفهوم اول:
همانطور که می دانیم در این معنا سکته مغزی به معنای چرخه به همین دلیل نام دستاوردهای موتور شش زمانه با توجه به فرایند چرخه شش آن می باشد. در آغاز از روش، گرمای از دست رفته از نرمال اتو چرخه موتور چهار زمانه است و به قدرت و قدرت اضافی مورد استفاده قرار گرفته و خروجی به معنی سکته مغزی است که مقدار حرارت از دست رفته توسط موتور چهار زمانه طبیعی استفاده می شود برای اضافه کردن در دو چرخه های اضافی به موتور شش زمانه. این به این معنا نیست که موتور شش زمانه از دو موتور ساخته شده است، در واقع آن را در واقع فقط یک تغییر اندک به موتور های چهار زمانه با اضافه کردن دو حرکت اضافی و یا در چرخه 'درک ساده تر از پیستون در احتراق اتاق یا استوانه است.
پس چه هستند دو سکته مغزی اضافی شامل:؟
همانطور که می دانیم، موتور چهار زمانه، چهار چرخه، دو چرخه هر یک برای مصرف و اگزوز است. خوب شش زمانه با این حال دارای سه (3) چرخه هر که بدان معنی است که پیستون در این نوع موتور به سمت بالا میرود و پایین سه (3) بار و برای هر یک از مصرف سوخت است. بنابراین در علاوه بر این به موتور های چهار زمانه است که تنها یک سکته مغزی قدرت است که مصرف سوخت، شش زمانه دارای دو مصرف قدرت قبل از احتراق است که برای اولین بار از مصرف سوخت و دوم متشکل از یا هوا یا بخار می باشد. این مفهوم از موتور شش زمانه نیز دارای سه (3) طرح جداگانه:
شش زمانه Crower موتور (در ایالات متحده آمریکا توسط بروس Crower اختراع)
(توسعه یافته توسط شرکت سویس، Bajulas SA) موتور Bajulaz
شش زمانه Velozeta موتور (که توسط دانشکده مهندسی در Trivandrum توسعه، هند)
مفهوم دوم:
مفهوم دیگر از این نوع موتور شش زمانه از نه یکی، بلکه دو پیستون مخالف یکدیگر در یک محفظه احتراق و یا سیلندر استفاده می کند. در این مفهوم با این حال، پیستون مخالف حرکت می کند، تنها نیمی از میزان چرخه پیستون اصلی در نتیجه با اضافه کردن تا در مجموع از شش پیستون حرکت در هر چرخه. پیستون دوم تولید و یا پیستون مخالف در این مورد جایگزین توابع از دریچه نرمال موتور چهار زمانه که در آن و در نتیجه تولید افزایش در نسبت تراکم از سیستم است. این مفهوم همچنین دارای دو طرح تقسیم، هر دو به طور مستقل در حال توسعه:
سر موتور بییر (اختراع توسط یک استرالیایی به نام مالکوم بییر)
پمپ شارژ آلمانی (اختراع هلموت Kottmann)
مطلب 2
The six-stroke engine
Introduction
Most internal combustion engines operating on different cycles, with a common plan to place a bomb in a cylinder after the compression is done. The result is that gas expansion laid directly on the piston (it does) and rotate the crankshaft 180 degrees.
Due to the mechanical design, as well as the six-stroke engine is an internal combustion engine. Although the thermodynamic cycle and a modified cylinder head with two supplementary chambers are entirely distinct. A combustion chamber and a compression chamber air heating both cylinders are separated. Cylinder combustion takes place inside the combustion chamber and it does not help immediately on the piston 180 degrees of crankshaft rotation during the explosion (work) is removed.
The combustion chamber is totally enclosed heating chamber. The heat transfer through the walls of the combustion chamber is in communication with the heating chamber, the chamber pressure is increased heating and power production is complementary to the work.
The six-stroke engine advantages:
• Achieve thermal efficiency of 50% (30% for internal combustion engines)
• Reduce fuel consumption by over 40%
• reduce pollution, heat, sound, chemical
• Two useful classes in a six-course
• Direct injection optimizes fuel combustion at any speed vehicle
موتورهای شش زمانه
مقدمه
عملیات سیکل های مختلف بیشتر موتورهای احتراق داخلی فعلی، دارای یک طرح رایج است به این صورت که انفجار در یک سیلندر پس از تراکم انجام می شود. نتیجه ان است که انبساط گاز مستقیما روی پیستون اثر گذاشته (کار انجام می دهد) و میل لنگ را 180 درجه بچرخاند.
با توجه به طراحی فنی و مکانیکی، موتور شش زمانه همانند موتورهای احتراق داخلی می باشد. اگر چه سیکل ترمودینامیکی و یک سر سیلندر اصلاح شده همراه دو اتاق اضافی ان را به کلی متمایز می کند. یک محفظه ی احتراق و یک محفظه ی تراکم( گرمکن هوا) هر دو از سیلندر جدا هستند. احتراق درون سیلندر رخ نمی دهد اما در محفظه ی احتراق کمکی هم فوری روی پیستون اثر نمی گذارد و زمان ان از 180 درجه ی چرخش میل لنگ، در زمان انفجار(کار) جدا می باشد.
محفظه ی احتراق به طور کلی توسط محفظه ی گرمکن احاطه شده است. با تبادل گرما از طریق دیواره های محفظه ی احتراق که با محفظه ی گرمکن در ارتباط است، فشار محفظه ی گرمکن افزایش می یابد و قدرت مکملی برای کار تولید می شود.
مزایای موتور شش زمانه:
• رسیدن به راندمان حرارتی % 50 (%30برای موتورهای احتراق داخلی فعلی)
• کاهش مصرف سوخت با بیش از %40
• کاهش الودگی حرارتی، صوتی، شیمیایی
• دو کورس مفید کار در طی شش کورس
• پاشش مستقیم و بهینه ی سوخت احتراق در هر سرعتی از خودرو
• Multiple fuel
The six-stroke engine vehicles will be a dramatic reduction in fuel consumption and emissions.
Design and performance of the six-stroke engine:
External combustion cycle. Diagram shows the interconnection of the eight six-stroke cycle.
The first four-cycle external combustion process:
Process 1: Intake of pure air into the cylinder (dynamic process)
Process 2: density of pure air in the heating chamber (dynamic process)
Process 3: Keep the pressure pure air in the closed chamber where most of the heat exchange with the walls of the combustion chamber occurs (static process because it does not work directly on the crankshaft.) Rises temperature.
Process 4: Expansion of the hot air balloons, the works. (Dynamic event). During the four-cycle process, pure air is never in direct contact with the fuel and spark.
The second four-cycle internal combustion.
Event 5: Re-condensation of pure heated air in the combustion chamber (dynamic)
Process 6: fuel injection and combustion in the combustion chamber, with no direct impact on the crankshaft (static process)
سوخت چند گانه
در خودروهای با موتور شش زمانه شاهد کاهش چشمگیر مصرف سوخت و انتشار الودگی خواهیم بود.
طراحی و عملکرد موتور های شش زمانه:
در سیکل شش زمانه، دو محفظه ی اضافی اجازه می دهند هشت فرایند که نتایج یک سیکل کامل است همزمان عمل کنند یعنی در یک لحظه دو فرایند همزمان رخ میدهد : دو سیکل چهار فرایندی برای هر کدام از سیکل ها،یک سیکل احتراق داخلی و یک سیکل احتراق خارجی. نمودار پیوستگی هشت فرایند را در سیکل شش زمانه نشان می دهد.
اولین سیکل چهار فرایندی احتراق خارجی:
فرایند1 :مکش هوای خالص درون سیلندر(فرایند دینامیکی)
فرایند 2: تراکم هوای خالص در محفظه ی گرمکن(فرایند دینامیکی)
فرایند3 : نگه داشتن فشار هوای خالص در محفظه ی بسته جایی که بیشترین تبادل گرما با دیواره های محفظه ی احتراق رخ می دهد(فرایند استاتیک چون مستقیما روی میل لنگ اثر نمی گذارد.) دمای هوا بالا می رود.
فرایند4 : انبساط هوای فوق داغ درون سیلندر، که کار انجام می دهد.(فرایند دینامیک). طی این سیکل چهار فرایندی، هوای خالص هرگز در تماس مستقیم با سوخت و شمع نمی باشد.
دومین سیکل چهار فرایندی که احتراق داخلی می باشد.
فرایند5: تراکم مجدد هوای خالص گرم درون محفظه ی احتراق(فرایند دینامیک)
فرایند6 : تزریق سوخت و احتراق در محفظه ی احتراق، بدون تاثیر مستقیم روی میل لنگ (فرایند استاتیک)
Process 7: combustion gas expands and gets the job done. (Dynamic)
Event 8: exhaust combustion gases (dynamic) During these four, the air directly to the heat source (fuel) is calling.
Two-chamber and four-valve cylinder head, two of which are conventional (intake and exhaust). Two heavy-duty valves are made of heat-resisting material. Valves in the combustion chamber and the hot air can be opened under pressure. Both valves mounted on a piston that helps suppress the pressure on the valve.'s Six-stroke cycle camshaft speed is a third crankshaft.
The walls of the combustion chamber when the engine is running, are glowing. Air-heating chamber, the combustion chamber surrounds. Small thickness allows the heat exchanger to the heating chamber. Air-heating chamber of the cylinder head insulated to reduce heat loss. (To introduce a simpler engine design detail is not explained.)
All the heat is transferred to the combustion chamber to chamber heater. The work is divided into two phases, resulting in less pressure on the piston and smooth for better performance.They also burn the air-fuel mixture in diesel engines or gas is commonly observed to prevent.
Compression ratio in the combustion chamber and the heater is different. Compression ratio combustion chamber heater is more on foreign works and is supported exclusively by pure air. Lower combustion chamber compression ratio that works on an internal combustion cycle.
For easy engine starting in cold weather, it has been heated in the combustion chamber of a spark.
فرایند7 : گازهای احتراق منبسط می شوند و کار انجام می شود. (فرایند دینامیک)
فرایند8: تخلیه گازهای احتراق (فرایند دینامیک) در طی این چهار فرایند، هوا مستقیما با منبع گرما (سوخت) تماس دارد.
سر سیلندر دو محفظه و چهار سوپاپ که دو تای ان متداول هستند،(برای مکش و تخلیه). دو سوپاپ دیگر از مواد پایدار حرارت دادن مخصوص کارسنگين ساخته شده. سوپاپها در طی مرحله احتراق و گرم کردن هوا می توانند تحت فشار محفظه ها باز شوند. روی هر دو سوپاپ یک پیستون نصب شده که فشار روی سوپاپ ها را خنثی میکند.در سیکل شش زمانه، سرعت میل بادامک یک سوم میل لنگ است.
دیواره های محفظه ی احتراق هنگامی که موتور روشن است، سوزان هستند. محفظه ی گرم کن هوا، محفظه ی احتراق را احاطه کرده است. ضخامت کم دیواره اجازه تبادل حرارت با محفظه ی گرم کن را می دهد. محفظه ی گرم کن هوا از سر سیلندر عایق شده برای اینکه اتلاف حرارتی کاهش یابد.(برای معرفی ساده تر موتور، جز ئیات طرح توضیح داده نشده است.)
نظرات شما عزیزان: